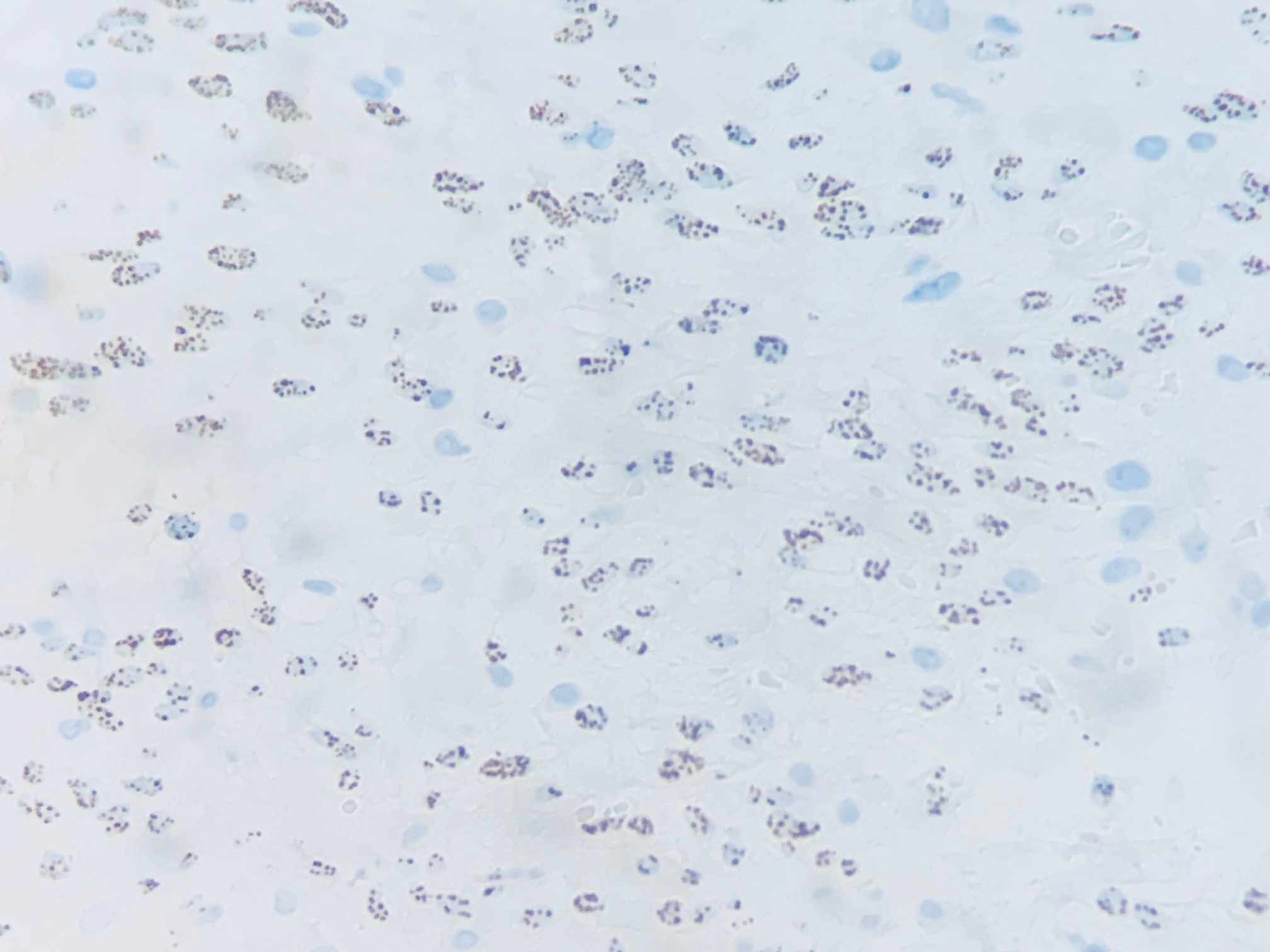
Bacillary angiomatosis and Kaposi's sarcoma in skin lesion of HIV positive patient
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.52226/revista.v31i112.179Keywords:
Bacillary angiomatosis, Kaposi’s sarcoma, HIV, AIDSAbstract
Bacillary angiomatosis (BA) is a rare infectious disease, caused by bacteria of the genus Bartonella spp, transmitted by vectors such as fleas, lice and mosquitoes. It causes different clinical syndromes in humans. In patients with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection with an LT CD4 + <100 cell/μL count, it is associated with the development of angiomatous lesions with neovascularization involving the skin and, with less frequency, mucous membranes, liver, spleen and bones. Kaposi's sarcoma (KS) is a neoplasm characterized by multifocal vascular hyperplasia of endothelial origin related to human herpes virus 8. It can also compromiso the skin, mucous membranes and viscera, with the epidemic variant being a marker disease of advanced HIV infection. The main clinical differential diagnosis for KS skin and mucosal lesions is the BA.
Herein we present a patient with HIV/AIDS disease that developed BA and KS concomitantly in the same skin lesion.
Downloads